13 LangChain 函数调用
- OpenAI LLMs 中的
函数调用(Function Calling)使得开发者可以对函数进行描述,而模型则可以用这些函数描述来生成函数调用参数,并与外部工具和 APIs 建立更为可靠、结构化的连接。1 - 开发者可以使用
JSON Schema定义函数,指导模型如何根据用户的输入信息来生成调用函数所需的参数,并调用函数。 函数调用会有非富多样的应用场景,例如:- 构建与外部工具或 APIs 交互的聊天机器人
- 把自然语言查询转换为 API 调用,以便和现有的
服务和数据库无缝整合 - 从非结构化的文本中提取结构化数据
函数调用会涉及到如下的步骤:- 调用包含
函数的模型 - 处理
函数响应 - 将
函数响应返回给模型,以进行进一步的处理货这生成更友好的用户响应
- 调用包含
- 根据 文心开发者文档,在文心 4.0 中,也增加了
函数调用的能力,其原理和使用和 OpenAI 相似。
13.1 大模型的时效性
当我们问大模型“明天天气怎么样”时,因为大模型训练语料的时效性问题,如果不依赖外部信息,大模型是很难回答这种问题的,如 图 13.1 所示。
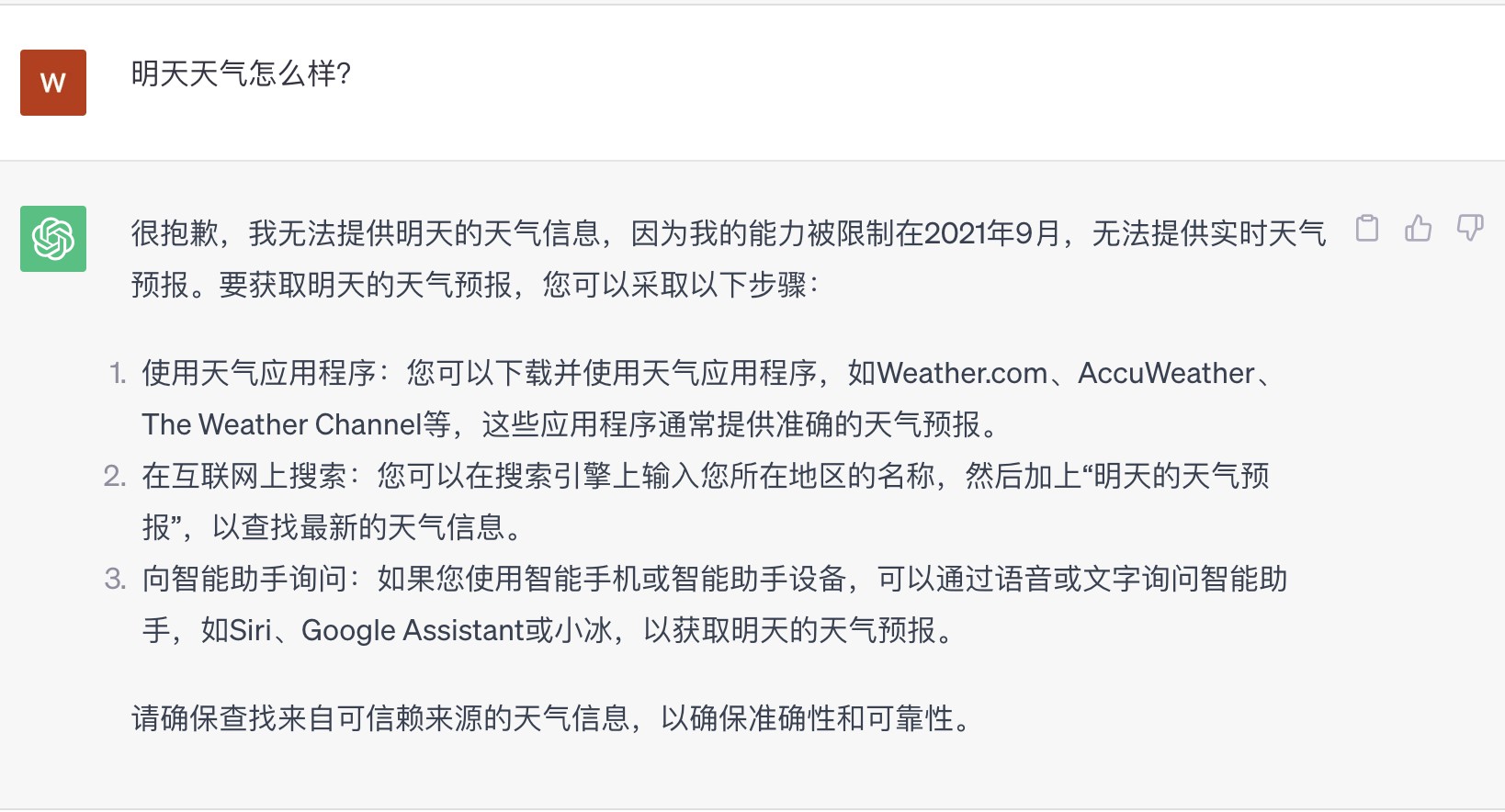

而 OpenAI 大语言模型提供的 函数调用 能力,恰恰非常完美的解决了类似的问题,从而使得大语言模型可以通过 函数调用 与外部系统通信,并获取更实时的信息,以解决类似的问题。
13.2 函数调用流程
OpenAI 开发的大语言模型(例如GPT-3.5-turbo-0613,GPT-4-0613)提供了一种名为 Function Calling(函数调用) 的创新功能。函数调用 使得开发人员能够在模型中对函数进行描述,然后模型可以利用这些描述来巧妙地为函数生成调用参数。
在 OpenAI 中,函数调用的步骤可以参考:图 13.2
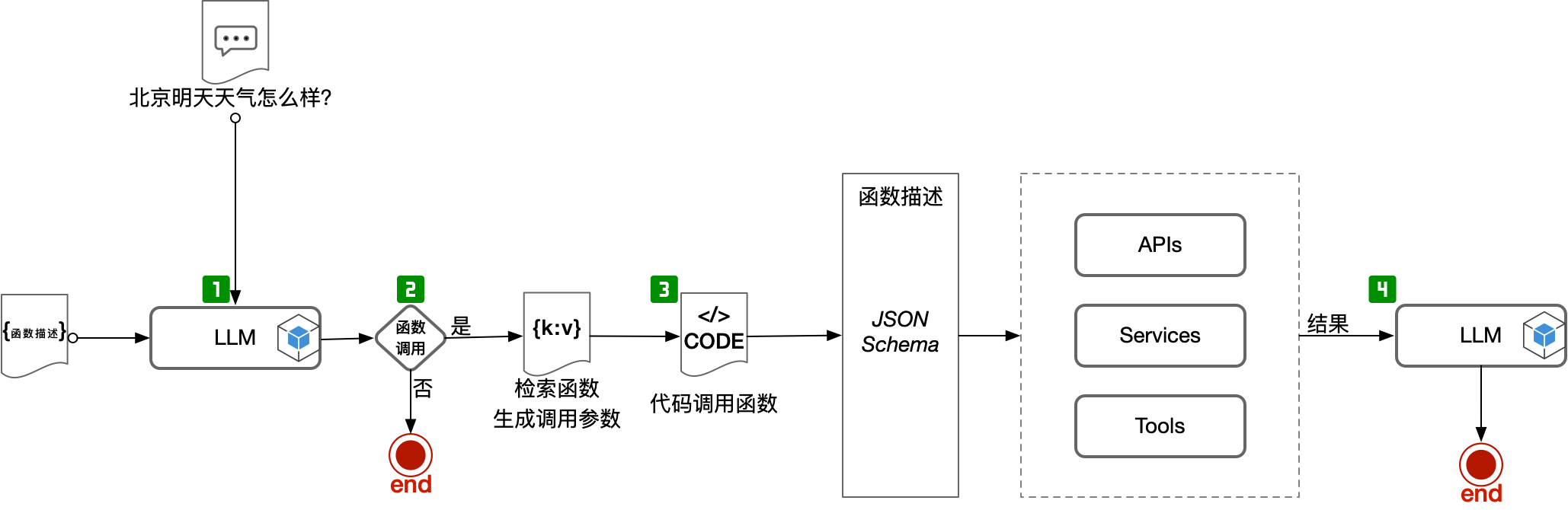
需要特别注意的是,大语言模型本身并不会调用我们预定的 函数,大语言模型仅仅是生成我们所要调用的函数的调用参数而已,具体调用函数的动作,需要我们在自己的应用代码中来实现。2
为什么模型不能直接调用函数?
利用 函数调用,LLMs 可以很方便的将自然语言指令转变为相关的函数调用,例如:可以把“给张三发一封邮件询问下他下周五下午是否需要一杯咖啡” 这样的提示转换为 send_email(to: string, body: string) 函数调用。
13.3 OpenAI 函数调用
13.3.1 OpenAI API
列表 13.1: 使用 OpenAI API 进行函数调用示例
import openai
import json
# Example dummy function hard coded to return the same weather
# In production, this could be your backend API or an external API
def get_current_weather(location, unit="celsius"):
"""Get the current weather in a given location"""
weather_info = {
"location": location,
"temperature": "27",
"unit": unit,
"forecast": ["sunny", "windy"],
}
return json.dumps(weather_info)
def run_conversation():
# Step 1: send the conversation and available functions to GPT
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "北京明天天气怎么样?"}]
functions = [
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
"unit": {"type": "string", "enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
]
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
messages=messages,
functions=functions,
function_call="auto", # auto is default, but we'll be explicit
)
print("---------step 1. the 1st LLMs response-----------")
print(response)
response_message = response["choices"][0]["message"]
# Step 2: check if GPT wanted to call a function
if response_message.get("function_call"):
# Step 3: call the function
# Note: the JSON response may not always be valid; be sure to handle errors
available_functions = {
"get_current_weather": get_current_weather,
} # only one function in this example, but you can have multiple
function_name = response_message["function_call"]["name"]
fuction_to_call = available_functions[function_name]
function_args = json.loads(response_message["function_call"]["arguments"])
function_response = fuction_to_call(
location=function_args.get("location"),
#unit=function_args.get("unit"),
)
print("---------step 2. function response-----------")
print(function_response)
# Step 4: send the info on the function call and function response to GPT
messages.append(response_message) # extend conversation with assistant's reply
messages.append(
{
"role": "function",
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response,
}
) # extend conversation with function response
print("---------step 3. final messages-----------")
print(messages)
second_response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
messages=messages,
) # get a new response from GPT where it can see the function response
return second_response
res = run_conversation()
print("---------step 4. final LLMs response-----------")
print(res)列表 13.2: 运行结果
---------step 1. the 1st LLMs response-----------
{
"id": "chatcmpl-7xnsEW2rSsec7Qd1FC60cKIT7TtuR",
"object": "chat.completion",
"created": 1694487422,
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
"choices": [
{
"index": 0,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"function_call": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"arguments": "{\n \"location\": \"北京\"\n}"
}
},
"finish_reason": "function_call"
}
],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 85,
"completion_tokens": 16,
"total_tokens": 101
}
}
---------step 2. function response-----------
{"location": "北京", "temperature": "27", "unit": null, "forecast": ["sunny", "windy"]}
---------step 3. final messages-----------
[{'role': 'user', 'content': '北京明天天气怎么样?'}, <OpenAIObject at 0x1082907c0> JSON: {
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"function_call": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"arguments": "{\n \"location\": \"北京\"\n}"
}
}, {'role': 'function', 'name': 'get_current_weather', 'content': '{"location": "\\u5317\\u4eac", "temperature": "27", "unit": null, "forecast": ["sunny", "windy"]}'}]
---------step 4. final LLMs response-----------
{
"id": "chatcmpl-7xnsFw2dssMs3R0aGVMmjB0cjLugZ",
"object": "chat.completion",
"created": 1694487423,
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613",
"choices": [
{
"index": 0,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "北京明天的天气预报是晴天,有很大的风。气温为27°C。"
},
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 77,
"completion_tokens": 30,
"total_tokens": 107
}
}13.3.2 OpenAI 函数调用 LLMChain
可以参考 LangChain 官方文档以在 LangChain 中使用 OpenAI 函数调用 的能力。3
列表 13.3: 使用 LangChain 实现函数调用
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.chains.openai_functions import (
create_openai_fn_chain,
)
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
import json
def get_current_weather(location: str, unit: str="celsius") -> str:
"""Get the current weather in a given location
Args:
location (str): location of the weather.
unit (str): unit of the tempuature.
Returns:
str: weather in the given location.
"""
weather_info = {
"location": location,
"temperature": "27",
"unit": unit,
"forecast": ["sunny", "windy"],
}
return json.dumps(weather_info)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0613")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("human", "{query}"),
]
)
chain = create_openai_fn_chain([get_current_weather], llm, prompt, verbose=True)
res = chain.run("What's the weather like in Beijing tomorrow?")
print("-------------The 1-st langchain result-------------")
print(res)
res_func = get_current_weather(res['location'])
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt, verbose=True)
res = chain.run("extract the tomorrow weather infomation from :%s, and answer the question: %s" % (res_func, "What's the weather like in Beijing tomorrow?"))
print(res)列表 13.3 的运行结果如下所示:
列表 13.4: 运行结果
> Entering new LLMChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
Human: What's the weather like in Beijing tomorrow?
> Finished chain.
-------------The 1-st langchain result-------------
{'location': 'Beijing', 'unit': 'metric'}
> Entering new LLMChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
Human: extract the tomorrow weather infomation from :{"location": "Beijing", "temperature": "27", "unit": "celsius", "forecast": ["sunny", "windy"]}, and answer the question: What's the weather like in Beijing tomorrow?
> Finished chain.
The weather in Beijing tomorrow is sunny and windy.在 create_openai_fn_chain 中,其第一个参数是一个函数列表,如果该列表只有 1 个函数时,则 create_openai_fn_chain 仅会返回大语言模型构造的调用该函数对应的参数。例如如上的例子,create_openai_fn_chain 仅返回了 {'location': 'Beijing', 'unit': 'metric'}。 而如果函数列表存在多个函数时,则会返回大语言模型分析之后所需要调用的函数名以及对应的参数,例如: {'name': 'get_current_weather', 'arguments': {'location': 'Beijing'}}。
列表 13.5: create_openai_fn_chain() 传递多个函数调用示例
# ...
def get_current_news(location: str) -> str:
"""Get the current news based on the location.'
Args:
location (str): The location to query.
Returs:
str: Current news based on the location.
"""
news_info = {
"location": location,
"news": [
"I have a Book.",
"It's a nice day, today."
]
}
return json.dumps(news_info)
# ...
chain = create_openai_fn_chain([get_current_weather, get_current_news], llm, prompt, verbose=True)
res = chain.run("What's the weather like in Beijing tomorrow?")
print("-------------The 1-st langchain result-------------")
print(res)列表 13.6: 运行结果
> Entering new LLMChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
Human: What's the weather like in Beijing tomorrow?
> Finished chain.
-------------The 1-st langchain result-------------
{'name': 'get_current_weather', 'arguments': {'location': 'Beijing'}}13.4 文心 4.0 函数调用
13.4.1 文心 API
在使用 文心 4.0 的函数调用之前,首先需要安装 qianfan 库:
pip install qianfan我们首先对本章前面提到的 get_current_news 和 get_current_weather 这两个函数实现其 JSON-Schema 描述:
列表 13.7: 待调用函数的函数描述
"""
@discribe: functions description.
@author: wangwei1237@gmail.com
"""
functions = [
{
"name": "get_current_news",
"description": "Get the current news based on the location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
"responses": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"news": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The current news based on the location.",
}
}
}
},
{
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
},
"unit": {"type": "string", "enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
"responses": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"temperature": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The temperature in the given location.",
}
}
}
},
]列表 13.8: 使用千帆 API 实现文心大模型的函数调用
- 1
- 指定采用的模型名称
- 2
- 和大模型交互的消息列表
- 3
- 告诉大模型我们有哪些函数可以调用,以及对应函数的具体描述,具体参见 列表 13.7
列表 13.8 的运行结果如下:
QfResponse(code=200, headers={...}, body={'id': 'as-cvbbn9t0vq', 'object': 'chat.completion', 'created': 1699708273, 'result': '', 'is_truncated': False, 'need_clear_history': False, 'function_call': {'name': 'get_current_news', 'thoughts': '用户想要知道北京的新闻。我可以使用get_current_news工具来获取这些信息。', 'arguments': '{"location":"北京"}'}, 'usage': {...})通过结果我们可以发现,文心大模型的 函数调用 和 OpenAI 的 函数调用 虽然不完全一致,但是还是非常相似的。对于有可以调用的函数时,文心大模型的返回结果中的 resp.result 为空,同时用 resp.function_call 存储针对当前问题,经过大模型分析后可以调用的函数以及调用函数时所用到的参数。具体接下来的函数调用过程,就和 OpenAI 一致了,可以参考 列表 13.1。
13.4.2 文心函数调用 LLMChain
目前,LangChain 并不支持像 列表 13.5 那样,通过 create_openai_fn_chain() 来进行函数调用。如果要实现该通能,需要对 LangChain 进行扩展,增加 create_ernie_fn_chai()。可以参照 create_openai_fn_chain() 来实现 create_ernie_fn_chain(),具体需要修改的代码参考:feat: add ERNIE-Bot-4 Function Calling。
feat: add ERNIE-Bot-4 Function Calling 已经合入 LangChain 的代码,LangChain 已经原生支持文心大模型的 函数调用 功能。为了兼容 QianfanChatEndpoint,我们对 create_ernie_fn_chain() 进行了升级,具体参见:langchain/pull/14275。
因为文心大模型的返回有自己的特性,在调用文心 API 时,对于存在 functions 参数的场景,其请求结果中的 function_call 字段是独立于 result 字段单独存在的。
QfResponse(code=200, headers={...}, body={'id': 'as-cvbbn9t0vq', 'object': 'chat.completion', 'created': 1699708273, 'result': '', 'is_truncated': False, 'need_clear_history': False, 'function_call': {'name': 'get_current_news', 'thoughts': '用户想要知道北京的新闻。我可以使用get_current_news工具来获取这些信息。', 'arguments': '{"location":"北京"}'}, 'usage': {...})而当前 LangChain 中对 LLM 返回的解析一般是对结果中的 result 字段进行解析。因此,要使用文心大模型的 函数调用 能力,同时还需要对 ErnieBotChat 进行升级。
def _create_chat_result(self, response: Mapping[str, Any]) -> ChatResult:
if 'function_call' in response:
function_call_str = '{{"function_call": {}}}'.format(
json.dumps(response.get("function_call")))
generations = [
ChatGeneration(message=AIMessage(content=function_call_str))
]
else:
generations = [
ChatGeneration(message=AIMessage(content=response.get("result")))
]
#...def _create_chat_result(self, response: Mapping[str, Any]) -> ChatResult:
if "function_call" in response:
additional_kwargs = {
"function_call": dict(response.get("function_call", {}))
}
else:
additional_kwargs = {}
generations = [
ChatGeneration(
message=AIMessage(
content=response.get("result"),
additional_kwargs={**additional_kwargs},
)
)
]
# ...完成如上的修改之后,可以像 列表 13.5 那样来简化大语言模型的 函数调用 过程。
列表 13.9: 使用 ErnieBotChat 执行文心大模型的函数调用
from langchain.chat_models import ErnieBotChat
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.chains.ernie_functions import (
create_ernie_fn_chain,
)
llm = ErnieBotChat(model_name="ERNIE-Bot-4")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("human", "{query}"),
]
)
chain = create_ernie_fn_chain([get_current_weather, get_current_news], llm, prompt, verbose=True)
res = chain.run("北京今天新闻是什么?")
print(res)列表 13.10: 使用 QianfanChatEndpoint 执行文心大模型的函数调用
ffrom langchain_community.chat_models import QianfanChatEndpoint
from langchain_core.prompts.chat import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
)
from langchain.chains.ernie_functions import (
create_ernie_fn_chain,
)
llm = QianfanChatEndpoint(model="ERNIE-Bot-4")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("human", "{query}"),
]
)
chain = create_ernie_fn_chain([get_current_weather, get_current_news], llm, prompt, verbose=True)
res = chain.run("北京今天新闻是什么?")
print(res)> Entering new LLMChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
Human: 北京今天新闻是什么?
> Finished chain.
{'name': 'get_current_news', 'thoughts': '用户想要知道北京今天的新闻。我可以使用get_current_news工具来获取这些信息。', 'arguments': {'location': '北京'}}接下来,根据文心大模型的返回内容,同时根据之前所述的 OpenAI 的 函数调用 方式来调用大模型返回的函数并获取对应信息即可。
13.5 根据 LLM 的返回调用对应函数
如前所述,LLMs 会根据当前的信息返回它认为我们应该调用的函数以及函数对应的参数,具体的函数执行还是需要我们手动执行。为了进一步简化该过程,我们对这个过程进行了抽象,具体如 列表 13.11。
列表 13.11: utils.call_function.call_function()
# !/usr/bin/env python3
"""
@discribe: The function running for Ernie-Bot-4 Function Calling.
@author: wangwei1237@gmail.com
"""
from typing import (
Any,
Callable,
Dict,
Sequence,
Type,
Union,
)
from langchain.chains.ernie_functions import (
convert_to_ernie_function,
)
from langchain.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel
from langsmith.run_helpers import traceable
1@traceable(run_type="tool")
def call_function(functions: Sequence[Union[Dict[str, Any], Type[BaseModel], Callable]],
fc_by_llm: dict) -> str:
"""Calling the function and return the result."""
if not fc_by_llm or "name" not in fc_by_llm or "arguments" not in fc_by_llm:
return ""
func_list = [f for f in functions if f.__name__ == fc_by_llm["name"]]
if len(func_list) != 1:
return ""
func = func_list[0]
func_args_keys = convert_to_ernie_function(func)["parameters"]["properties"].keys()
fc_args_by_llm = fc_by_llm["arguments"]
func_args = {
key: fc_args_by_llm[key] for key in func_args_keys if key in fc_args_by_llm
}
res = func(**func_args)
return res- 1
- 方便 LangSmith 可以追踪到函数调用,方便 DEBUG。
通过文心大模型的函数调用解决我们的问题的完整代码如 列表 13.12 所示。
列表 13.12: 文心大模型利用函数调用解决问题
# !/usr/bin/env python3
"""
@discribe: demo for the Ernie-Bot-4 Function Calling.
@author: wangwei1237@gmail.com
"""
import json
import uuid
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.chains.ernie_functions import (
create_ernie_fn_chain,
)
from langchain_community.chat_models import QianfanChatEndpoint
from langchain_core.prompts.chat import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
)
from utils.call_function import call_function
run_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
print(run_id)
def get_current_news(location: str) -> str:
"""Get the current news based on the location.'
Args:
location (str): The location to query.
Returs:
str: Current news based on the location.
"""
news_info = {
"location": location,
"news": [
"I have a Book.",
"It's a nice day, today."
]
}
return json.dumps(news_info)
def get_current_weather(location: str, unit: str="celsius") -> str:
"""Get the current weather in a given location
Args:
location (str): location of the weather.
unit (str): unit of the tempuature.
Returns:
str: weather in the given location.
"""
weather_info = {
"location": location,
"temperature": "27",
"unit": unit,
"forecast": ["sunny", "windy"],
}
return json.dumps(weather_info)
llm = QianfanChatEndpoint(model="ERNIE-Bot-4")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("human", "{query}"),
]
)
chain = create_ernie_fn_chain([get_current_weather, get_current_news], llm, prompt, verbose=True)
res = chain.invoke({"query": "北京今天的新闻是什么?"}, config={"metadata": {"run_id": run_id}})
print(res)
res = res["function"]
if res:
res_cf = call_function([get_current_news, get_current_weather], res)
print(res_cf)
prompt_2 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("human", "从 {function} 中,我们得到如下信息:{function_res},那么 {query}"),
]
)
chain_2 = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt_2, verbose=True)
res_2 = chain_2.invoke({"function": res["name"], "function_res": res_cf, "query": "北京今天的新闻是什么?"}, config={"metadata": {"run_id": run_id}})
print(res_2)
列表 13.12 的执行结果如下所示:
> Entering new LLMChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
Human: 北京今天的新闻是什么?
> Finished chain.
> Entering new LLMChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
Human: 从 get_current_news 中,我们得到如下信息:{"location": "\u5317\u4eac", "news": ["I have a Book.", "It's a nice day, today."]},那么 北京今天的新闻是什么?
> Finished chain.
根据提供的信息,`get_current_news` 返回的数据中,"北京"的新闻有两条,分别是 "I have a Book." 和 "It's a nice day, today."。所以,北京今天的新闻包括这两条信息。整个函数调用的的整个过程如 图 13.3 所示。
