12.5 Using multiple ingress controllers
Since different ingress implementations provide different additional functionality, you may want to install multiple ingress controllers in a cluster. In this case, each Ingress object needs to indicate which ingress controller should process it. Originally, this was accomplished by specifying the controller name in the kubernetes.io/ingress.class annotation of the Ingress object. This method is now deprecated, but some controllers still use it.
Instead of using the annotation, the correct way to specify the controller to use is through IngressClass objects. One or more IngressClass objects are usually created when you install an ingress controller.
When you create an Ingress object, you specify the ingress class by specifying the name of the IngressClass object in the Ingress object’s spec field. Each IngressClass specifies the name of the controller and optional parameters. Thus, the class you reference in your Ingress object determines which ingress proxy is provisioned and how it’s configured. As you can see in the next figure, different Ingress objects can reference different IngressClasses, which in turn reference different ingress controllers.
Figure 12.9 The relationship between Ingresses, IngressClasses, and Ingress controllers
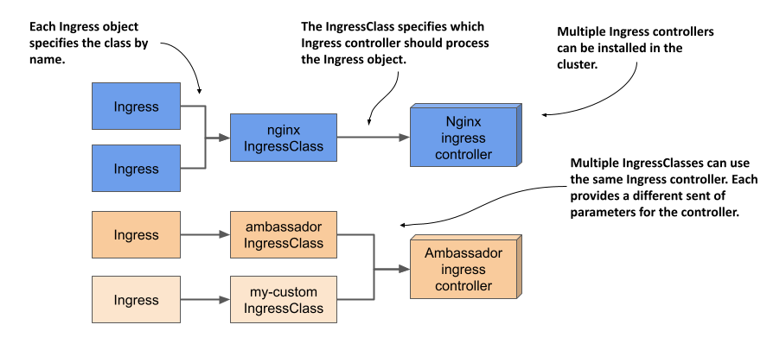
12.5.1 Introducing the IngressClass object kind
If the Nginx ingress controller is running in your cluster, an IngressClass object named nginx was created when you installed the controller. If other ingress controllers are deployed in your cluster, you may also find other IngressClasses.
Finding IngressClasses in your cluster
To see which ingress classes your cluster offers, you can list them with kubectl get:
$ kubectl get ingressclasses
NAME CONTROLLER PARAMETERS AGE
nginx k8s.io/ingress-nginx <none> 10h
The output of the command shows that a single IngressClass named nginx exists in the cluster. Ingresses that use this class are processed by the k8s.io/ingress-nginx controller. You can also see that this class doesn’t specify any controller parameters.
Inspecting the YAML manifest of an IngressClass object
Let’s take a closer look at the nginx IngressClass object by examining its YAML definition:
$ kubectl get ingressclasses nginx -o yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: IngressClass
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
controller: k8s.io/ingress-nginx
As you can see, this IngressClass object specifies nothing more than the name of the controller. Later you’ll see how you can also add parameters for the controller to the object.
12.5.2 Specifying the IngressClass in the Ingress object
When you create an Ingress object, you can specify the class of the ingress using the ingressClassName field in the spec section of the Ingress object, as in the following listing.
Listing 12.12 Ingress object referencing a specific IngressClass
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: kiada
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
...
The Ingress object in the listing indicates that its class should be nginx. Since this IngressClass specifies k8s.io/ingress-nginx as the controller, the Ingress from this listing is processed by the Nginx ingress controller.
Setting the default IngressClass
If multiple ingress controllers are installed in the cluster, there should be multiple IngressClass objects. If an Ingress object doesn’t specify the class, Kubernetes applies the default IngressClass, marked as such by setting the ingressclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class annotation to "true".
12.5.3 Adding parameters to an IngressClass
In addition to using IngressClasses to specify which ingress controller to use for a particular Ingress object, IngressClasses can also be used with a single ingress controller if it can provide different ingress flavors. This is achieved by specifying different parameters in each IngressClass.
Specifying parameters in the IngressClass object
The IngressClass object doesn’t provide any fields for you to set the parameters within the object itself, as each ingress controller has its own specifics and would require a different set of fields. Instead, the custom configuration of an IngressClass is typically stored in a separate custom Kubernetes object type that’s specific to each ingress controller implementation. You create an instance of this custom object type and reference it in the IngressClass object.
For example, AWS provides an object with kind IngressClassParams in API group elbv2.k8s.aws, version v1beta1. To configure the parameters in an IngressClass object, you reference the IngressClassParams object instance as shown in the following listing.
Listing 12.13 Referring to a custom parameters object in the IngressClass
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: IngressClass
metadata:
name: custom-ingress-class
spec:
controller: ingress.k8s.aws/alb
parameters:
apiGroup: elbv2.k8s.aws
kind: IngressClassParams
name: custom-ingress-params
In the listing, the IngressClassParams object instance that contains the parameters for this IngressClass is named custom-ingress-params. The object kind and apiGroup are also specified.
Example of a custom API object type used to hold parameters for the IngressClass
The following listing shows an example of an IngressClassParams object.
Listing 12.14 Example IngressClassParams object manifest
apiVersion: elbv2.k8s.aws/v1beta1
kind: IngressClassParams
metadata:
name: custom-ingress-params
spec:
scheme: internal
ipAddressType: dualstack
tags:
- key: org
value: my-org
With the IngressClass and IngressClassParams objects in place, cluster users can create Ingress objects with the ingressClassName set to custom-ingress-class. The objects are processed by the ingress.k8s.aws/alb controller (the AWS Load Balancer controller). The controller reads the parameters from the IngressClassParams object and uses them to configure the load balancer.
Kubernetes doesn’t care about the contents of the IngressClassParams object. They’re only used by the ingress controller. Since each implementation uses its own object type, you should refer to the controller’s documentation or use kubectl explain to learn more about each type.